
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
An intermediate circuit between the main circuit and the control circuit for amplifying the signal of the control circuit is called a drive circuit. The drive circuit can be divided into voltage drive and current drive. So what is the difference between voltage drive and current drive?
By definition:
Some electronic devices, such as tubes and FETs, have very low input currents, both nanoampere and even picoampere, which are negligible. The output state is completely dependent on the input voltage level, including the use of FETs. The logic devices (CMOS circuits) made by the process are all voltage driven.
The output state of an electronic device such as a bipolar transistor depends entirely on the magnitude of the input current. The input current is typically microampere to milliampere, including logic devices (TTL circuits) fabricated using bipolar transistor processes. Current driven.
It should be specially noted that although the TTL circuit indicates the high and low logic levels, pulling a high-level gate low to a low level requires a driving capability of 0.3 mA.

Bipolar transistor
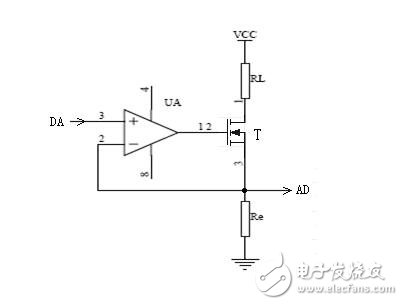
Voltage-driven, such as: FET, because its internal resistance is very large, the current is small when applying voltage control, which is approximately zero, so it can be understood as: voltage drive;
Current driven such as: ordinary NPN, PNP type triode, because its internal resistance is small, the current is relatively large when voltage control is applied (generally, the low power has more than 100uA, the high power can reach more than 20mA), so Understood as: current drive;
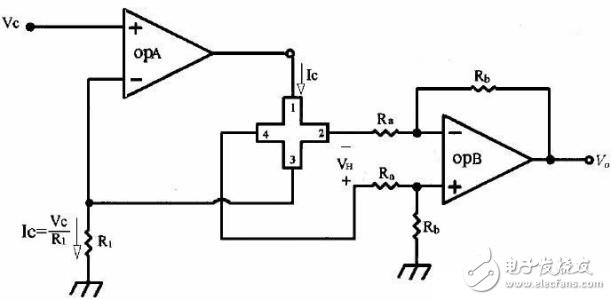
Current drive
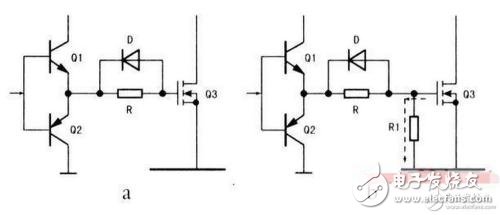
Voltage-driven, such as: FET, it is controlled by the voltage applied to the G and S terminals (microscopic is the electric field) to control the width of the internal channels of D and S (ie, the channel is variable) to control the currents across D and S;
Current-driven, such as ordinary NPN and PNP transistors, control the current flow inside C and E (that is, the channel does not change) by the current applied to the B and E terminals (microscopic is the flow of electrons).
to sum upSimply speaking, the current drive is based on the magnitude of the drive current and outputs different power. The common one is the common triode power amplifier circuit. The voltage drive outputs different power according to the driving voltage. It is used in the common field effect triode power amplifier circuit.
Enviar e-mail para este fornecedor

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.