
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
1 review
The electric vehicle drive motor and its control system are the heart of the electric vehicle and are components that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the vehicle. Its mission is to efficiently convert the energy of the power battery into the kinetic energy of the wheel or the kinetic energy on the wheel into the power battery under the control of the driver. The mutual transformation of electrical energy and mechanical energy is formed by an air gap between the rotor and the stator of the motor.
2 pure electric vehicle motor drive system classification
Single motor: There is a differential speed reducer, no clutch and transmission, and a motor with a low speed and large torque and a large speed change region is required, and the capacity of the motor and the inverter is large.
Dual motors: front and rear drive and two-wheel motor, two-wheel motor and inverter manufacturing costs.
Four-wheel hub motor: Compact structure and highest efficiency.
3 New energy vehicle drive motor performance
Car running function, comfort, adapt to the environment, driving range of one charge, temperature resistance, moisture resistance, low noise, simple structure, convenient maintenance, etc.
(1) Low speed and large torque characteristics and constant power characteristics in a wide range
(2) High efficiency and low loss over the entire operating range
(3) Small size and light weight
(4) Good reliability, high temperature and moisture resistance, and long-term work in harsh environments.
(5) low price
(6) High voltage (maximum voltage, reduce motor size and harness size, reduce inverter cost)
(7) The electrical system is highly safe (according to the standards and regulations for the safety performance of the relevant vehicle electrical control.)
(8) High speed (small size, light weight)
(9) Realize braking energy recovery and feedback battery when the vehicle is decelerating.
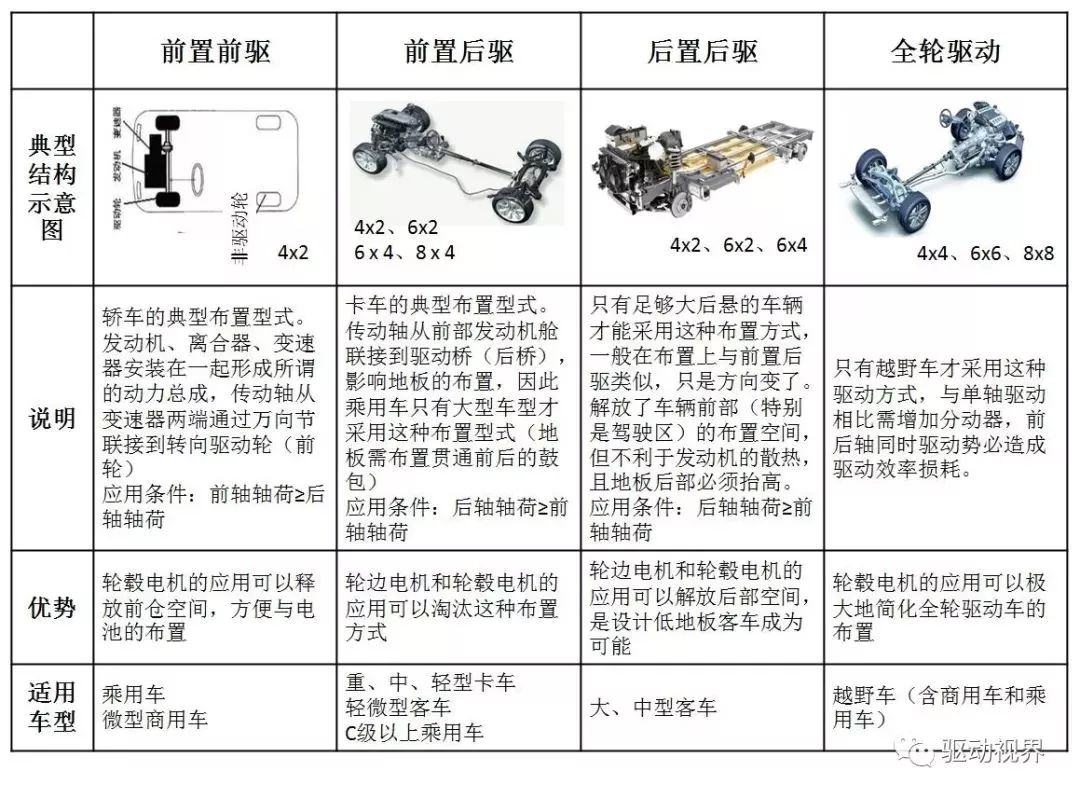
4 electric drive system structure
(1) Traditional drive system
The electric motor replaces the engine.
The transmission system of internal combustion engine vehicles is still used, including clutches, transmissions, drive shafts and drive axles.
There are various drive modes such as motor front, drive axle front (FF), motor front and drive axle rear (FR).
The structure is complicated and the efficiency is low, and the performance of the motor cannot be fully utilized.
(2) Simplified traditional drive system
With a fixed speed ratio reducer, the clutch can be removed, which can reduce the quality of the mechanical transmission and reduce its volume.

(3) Motor-drive axle integral drive system
It is similar to the arrangement of the engine with the lateral front and front wheel drive of the engine.
The motor, the fixed speed ratio reducer and the differential are integrated into one unit, and the two half shafts are connected to drive the wheel.
The transmission mechanism is compact, the transmission efficiency is high, and the installation is convenient, and it is most commonly used in small electric vehicles.

(4) Dual motor drive system
Two motors are driven by a fixed speed ratio reducer using two motors.
The speed of each motor can be independently adjusted and controlled to facilitate electronic differential speed without the need for a mechanical differential.
The advantages of the electronic differential are small size and light weight, which can achieve precise electronic control when the car turns and improve the performance of the electric vehicle. The disadvantage is that the initial cost is increased due to the addition of the motor and the power converter, and it is different. The reliability of precise control of two motors under conditions requires further development.

(5) Inner rotor electric wheel drive system
The motor is mounted in the wheel to form a hub motor that further reduces the transmission path from the motor to the drive wheel.
A high-speed inner rotor motor (approx. 10000r/min) is required, and a fixed speed ratio reducer is required to reduce the vehicle speed. Generally, a high reduction ratio planetary gear reduction device is installed between the motor output shaft and the wheel rim, and the input and output shafts can be arranged on the same axis.
The high speed inner rotor motor has the advantages of small size, light weight and low cost, but it requires a planetary gear shifting mechanism.

(6) Outer rotor electric wheel drive system
The low speed outer rotor motor is used to completely remove the shifting device.
The outer rotor of the motor is mounted directly on the wheel rim. The motor speed is equal to the wheel speed. The wheel speed and vehicle speed control are completely dependent on the motor speed control.
The low-speed outer rotor motor has a simple structure and does not require a gear shifting transmission mechanism, but has a large volume, high quality, and high cost.
5 DC motor
Advantages: The starting acceleration accelerates the traction, the control performance is good, the control system is simple, and the cost is low.
Disadvantages: The mechanical steering gear will generate sparks, the speed should not be too high, and the overload capability, speed range, power-to-volume ratio, power-to-mass ratio, system efficiency, and maintenance are limited.

Driving characteristics of DC motors
In the constant torque zone, the excitation current remains unchanged and the armature voltage is controlled to change the torque.
In the constant power zone, the armature voltage remains the same, changing the field current or the field weakening control torque.

Driving characteristics of DC motors
The characteristics of DC motors for electric vehicles should have
The armature shaft is extended to facilitate the installation of the tachometer pulse generator and the thrust shaft joint.
The rotor diameter should be designed to be smaller and the shaft length should be longer.
In order to facilitate heat dissipation, the armature slot is more than the actual one.
For periodic inspection and maintenance of commutator segments, brushes, etc., the inspection port should be made larger.
Due to the vibration, in order to prevent the brush from malfunctioning, the pre-compression force of the brush should be increased.
DC motors for electric vehicles need to be considered for high temperature resistance, vibration resistance, low loss, load fluctuation, small size and light weight, and maintenance-free operation.
6 AC motor
(1) Synchronous motor: The rotor speed is equal to the rotational speed of the stator rotating magnetic field.
It is divided into winding type and permanent magnet type.
(2) Asynchronous motor: The rotor speed is not equal to the rotational speed of the stator rotating magnetic field.
Advantages: simple structure, low price, reliable operation, convenient maintenance and high efficiency.
Disadvantages: low power factor.
The AC asynchronous motor for electric vehicles has the following characteristics:
High efficiency at high speed and low torque.
High torque at low speeds and a wide speed range.
It is easy to achieve high-speed rotation with a speed exceeding 10,000r/min.
Small and lightweight.
High reliability.
The manufacturing cost is low.
The simplification of the control device.

Drive characteristics of permanent magnet synchronous motor
Asynchronous motors are multivariable systems in which voltage, current, frequency, flux, and speed interact.
Speed control of asynchronous motor: vector control, direct torque control, speed control, variable frequency constant voltage control, adaptive control, efficiency optimization control, etc.
7 permanent magnet motor
According to the type of current input to the motor terminal, it can be divided into: permanent magnet DC motor, permanent magnet AC motor (permanent magnet brushless motor, no brush, slip ring or commutator)
According to the AC waveform permanent magnet brushless motor input to the motor terminal, it can be divided into: permanent magnet synchronous motor, permanent magnet brushless DC motor
The existing permanent magnet motors can be classified into four types: permanent magnet DC motor, permanent magnet synchronous motor, permanent magnet brushless DC motor and permanent magnet hybrid motor (the latter three are called permanent magnet brushless motors).
According to the position of the permanent magnet on the rotor, the permanent magnet synchronous motor can be divided into: built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor (SPM), external permanent magnet synchronous motor (IPM)
Need to study and solve the problem:
(1) Motor efficiency: low speed efficiency is low.
(2) The weak magnetic capability of the motor: the speed increases, the motor voltage rises, and the speed must be continuously increased. Only the stator current is adjusted to increase the speed by equivalent weakening. The magnetic circuit has a large magnetic resistance and a weak magnetic field capability.
advantage:
Higher "power/quality" ratio (no windings on the rotor, no copper consumption, low magnetic flux, and low iron loss at low loads).
Higher frequency, greater output torque.
The dynamic performance of the motor is good.
The motor's limit speed and braking performance are excellent.
Its cooling system is relatively simple.
The constant torque zone is relatively long.
The maximum motor speed is high and can reach 10000r/min.
High power density and good speed regulation performance.
High efficiency (90%~95%) in a wide speed range.
Disadvantages:
Magnetic flux adjustment is difficult.
Control systems have become more complex and costly.
Permanent magnet motors have a small power range.
When the vibration, high temperature and overload current act, the magnetic permeability of the permanent magnet material may be degraded or the demagnetization may occur.
The cost of the motor is high.
Permanent magnet materials have a demagnetization effect.
Poor corrosion resistance.
The magnetic field of the permanent magnet material is not variable, and the volume of the motor will increase correspondingly in order to increase the power of the motor.
8 hub motor
Hub motor drive
(1) Deceleration drive mode
Features: High speed operation, optional inner rotor motor, reducer.
Advantages: high power and efficiency ratio, small size, light weight, large torque, good climbing performance and stable low speed torque.
Disadvantages: It is difficult to achieve liquid lubrication. This wheel has fast wear and short life, is not easy to dissipate heat, and has high noise.
(2) Direct drive mode
Features: The outer rotor is mostly used, which requires the motor to have low speed and large torque and wide adjustment range.
Advantages: no reducer, compact structure, simple, small axial size, high efficiency and fast response.
Disadvantages: starting, windward, climbing, heavy load requires large current, easy to damage the battery and permanent magnets, the peak area of efficiency is small, and the efficiency drops sharply after the load current exceeds a certain value.
Cars that use a hub motor drive system have many advantages:
(1) Power control is changed from hard connection to soft connection.
(2) The driving force of each motor wheel is directly and independently controllable, and the power control is more flexible and convenient.
(3) It is easy to realize electric braking, electromechanical compound braking and braking energy feedback of each motor.
(4) The structure of the underframe is greatly simplified, and the overall layout of the vehicle and the freedom of design of the vehicle body are large. If the four-wheel motor drive system is introduced into the four-wheel steering technology (4WS), the vehicle's steering performance is improved, the turning radius is reduced, and even zero-radius steering is possible.
Technical advantages of the hub motor:
Omit a large number of transmission components, making the vehicle structure simpler, facilitating the layout of the battery pack, facilitating the layout of the floor, and making the floor structure simpler;
High transmission efficiency;
Light weight;
A variety of complex driving methods can be realized.
Technical disadvantages of the hub motor:
The hub motor greatly increases the unsprung mass and also increases the moment of inertia of the hub, which is detrimental to the handling performance of the vehicle.
The electric braking performance is limited, and it takes a lot of electric energy to maintain the braking system operation;
Since the electric braking capacity of the hub motor system is small and cannot meet the requirements of the braking performance of the entire vehicle, an additional mechanical braking system is required;
Without the vacuum pump driven by the traditional internal combustion engine, an electric vacuum pump is needed to provide brake boost, but it means greater energy consumption;
The working environment of the hub motor is harsh, and it faces many influences such as water and dust. It also has high requirements in terms of sealing. At the same time, it is also necessary to separately consider the heat dissipation problem for the hub motor.
Enviar e-mail para este fornecedor

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.